Automotive Telematics in 2026: Architecture, Regulations, Use-Cases & What Buyers Should Ask
Telematics has shifted from simple GPS tracking to a software-defined foundation for emergency services (eCall), remote diagnostics (UDS/DoIP), over-the-air (OTA) updates, usage-based insurance, and EV battery intelligence. Regulatory tailwinds (EU eCall 4G/5G, UNECE R155/R156, India AIS-140, US ELD), privacy laws (GDPR/CCPA/India DPDP), and 3G sunsets are forcing upgrades to LTE-M/LTE Cat-1 bis/5G with eSIM. According to KBV Research, the Global Automotive Telematics Market is set to reach USD 110.73 Bn by 2032 (CAGR 13.7%).
What exactly is “telematics” in 2026?
At a high level: an in-vehicle Telematics Control Unit (TCU) with cellular (now often eSIM), GNSS, secure storage, and a gateway to in-vehicle networks (CAN/LIN/FlexRay/Ethernet). On the software side, the stack covers device management (e.g., LwM2M), data transport (MQTT), remote diagnostics (UDS/DoIP), and security/OTA frameworks.
Key building blocks & standards
- UDS (ISO 14229) for diagnostics; DoIP (ISO 13400) to run diagnostics over IP/Ethernet.
- Automotive Ethernet (100BASE-T1 / 1000BASE-T1) to move high-bandwidth data inside the car.
- Device management & telemetry via OMA SpecWorks LwM2M and MQTT (ISO/IEC 20922).
- eSIM for vehicles using GSMA SGP.02 (M2M) for remote profile provisioning.
- Digital keys (smartphone-as-key) under Car Connectivity Consortium Digital Key.
Why telematics is a must-have now
Regulatory triggers
- EU eCall has been mandatory for new M1/N1 types since 2018—and the EU updated the rules in 2024/1180 to require 4G/5G-compatible eCall as 2G/3G retire.
- UNECE R155/R156 make cybersecurity management and safe OTA updates part of type approval in many markets.
- India AIS-140 mandates vehicle tracking + panic button for public service vehicles, with MoRTH/State implementations and VLT back-ends.
- US FMCSA ELD requires electronic logging devices for HOS compliance in commercial vehicles.
Network sunsets
3G has been shut down across the major US carriers (AT&T/T-Mobile/Verizon) and switch-offs are accelerating worldwide—pushing upgrades to LTE Cat-1 bis, LTE-M/NB-IoT, and 5G in TCUs.
V2X momentum
The FCC’s new 5.9 GHz rules formally pivot US ITS spectrum to C-V2X, clarifying parameters for roadside and in-vehicle units.
Market snapshot
- Size & growth:USD 44.96 Bn (2025) → 110.73 Bn (2032) at 13.7% CAGR.
- Who leads: Asia-Pacific holds the largest share; OEM-embedded telematics remains the dominant channel; embedded tech outpaces tethered.
Deep-dive: the modern telematics stack
Data capture & in-vehicle networking
- TCUs talk to ECUs over CAN and increasingly Ethernet (100/1000BASE-T1) for higher throughput (camera, OTA flashing). UDS provides services (read DTCs, firmware download), while DoIP moves those services over IP.
Connectivity & identity
- eSIM (GSMA SGP.02) enables remote profile swaps (e.g., roaming MVNOs for fleets), improving resilience vs single-carrier SIMs.
- For low-power peripherals (trailers, assets), OEMs increasingly add LTE-M/NB-IoT radios (3GPP IoT).
Telemetry, device management & OTA
- MQTT is the defacto telemetry bus; LwM2M covers remote config, FOTA, and lifecycle (bootstrap/registration).
- Vehicle-wide software update governance and traceability are regulated under UNECE R156.
Security & compliance
- NHTSA’s Cybersecurity Best Practices (2022) and UNECE R155 formalize threat modeling, vulnerability mgmt, and secure development/ops for connected vehicles.
Priority use-cases
- Safety & emergency: Automatic eCall with GNSS fix + crash data transfer to 112; migration to 4G/5G eCall is now codified.
- Remote diagnostics & predictive maintenance: UDS/DoIP to read DTCs and push firmware without a dealer visit.
- Fleet operations & compliance: AIS-140 (India) for public service vehicles; ELD (US) for HOS compliance.
- Insurance (UBI): High-fidelity trip/behavior scoring via OEM APIs/TCUs; governed by GDPR/CCPA/DPDP in respective regions.
- EV insights: Battery SoC/SOH, charging analytics, thermal alarms; coordination with energy services through the telematics cloud.
- Digital keys & access: CCC Digital Key for secure smartphone access and sharing.
- V2X-assisted awareness: C-V2X safety messages once markets deploy RSUs/OBUs under the new FCC framework.
Regional regulation cheat-sheet
European Union
- eCall baseline (2015/758) with 4G/5G update (2024/1180).
- UNECE R155/R156 adopted by many EU countries for cybersecurity/OTA.
- Data Act (2023/2854) sets horizontal rules for access/use of IoT data (including vehicles) with application dates from 12 Sept 2025 and emerging vehicle-data guidelines.
India
- AIS-140 mandate: VLT + SOS buttons for public service vehicles; MoRTH/States operate back-ends and empanel certified device makers.
- DPDP Act 2023 governs personal-data processing (telematics/UBI).
United States
- FCC ITS 5.9 GHz rules green-light C-V2X.
- FMCSA ELD is mandatory for covered commercial drivers.
- NHTSA Cybersecurity Best Practices (2022) inform OEM supplier controls.
Architecture patterns we recommend in 2026
Dual-mode connectivity strategy
Pair LTE Cat-1 bis or LTE-M for pervasive coverage with 5G where available; provision via eSIM to avoid single-carrier lock-in.
Diagnostics-first design
Ensure UDS services are routable via DoIP for remote ops (flash/patch/parameter changes) and field triage.
Standards-based device mgmt
Use LwM2M for bootstrap/firmware/telemetry and MQTT for streaming—helps with portability across hyperscalers.
Compliance by construction
Map your processes to UNECE R155/R156 + NHTSA best practices; keep audit trails and UL-style security testing artifacts where required by local regulators/AHJs.
Buyer’s RFP checklist
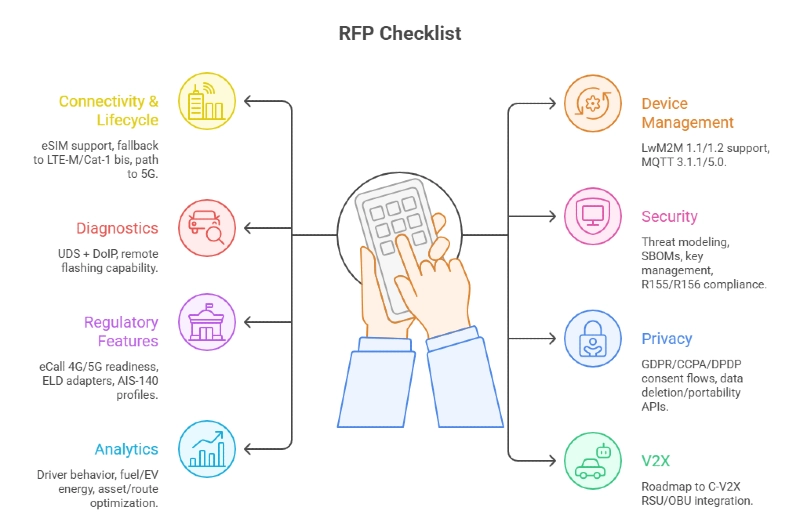
- Connectivity & lifecycle: eSIM (SGP.02) with multi-IMSI support; fallback to LTE-M/Cat-1 bis; path to 5G.
- Device mgmt: LwM2M 1.1/1.2 support (bootstrap, FOTA, objects); MQTT 3.1.1/5.0.
- Diagnostics: UDS (ISO 14229) + DoIP (ISO 13400-2:2025); remote flashing capability with access control.
- Security: Threat modeling, SBOMs, key management/HSM in TCU; compliance with R155; update controls per R156.
- Regulatory features: eCall 4G/5G readiness (EU), ELD (US) adapters, AIS-140 profiles (India).
- Privacy: GDPR/CCPA/DPDP consent flows; data deletion/portability APIs.
- Analytics: Driver behavior, fuel/EV energy, asset/route optimization; northbound export to data lake.
- V2X: Roadmap to C-V2X RSU/OBU integration under FCC parameters.
Common pitfalls
- 3G/2G dependency — legacy TCUs that can’t roam on LTE-M/Cat-1 bis will strand services as sunsets continue. Build migration plans now.
- Closed data models — avoid vendor lock-in by adopting LwM2M objects and well-documented MQTT topics.
- Security as a bolt-on — regulators treat cybersecurity and OTA as type-approval topics (R155/R156); treat them as first-class requirements.
KBV Research view of the market
Our latest analysis places the market at USD 110.73 Bn by 2032, with OEM-embedded solutions and APAC leading. Growth tracks mandates (eCall/AIS-140/ELD), software-defined vehicles, and new monetization (UBI, digital services). For commercial readers, the near-term ROI is strongest in fleet compliance, remote diagnostics, and EV energy optimization.